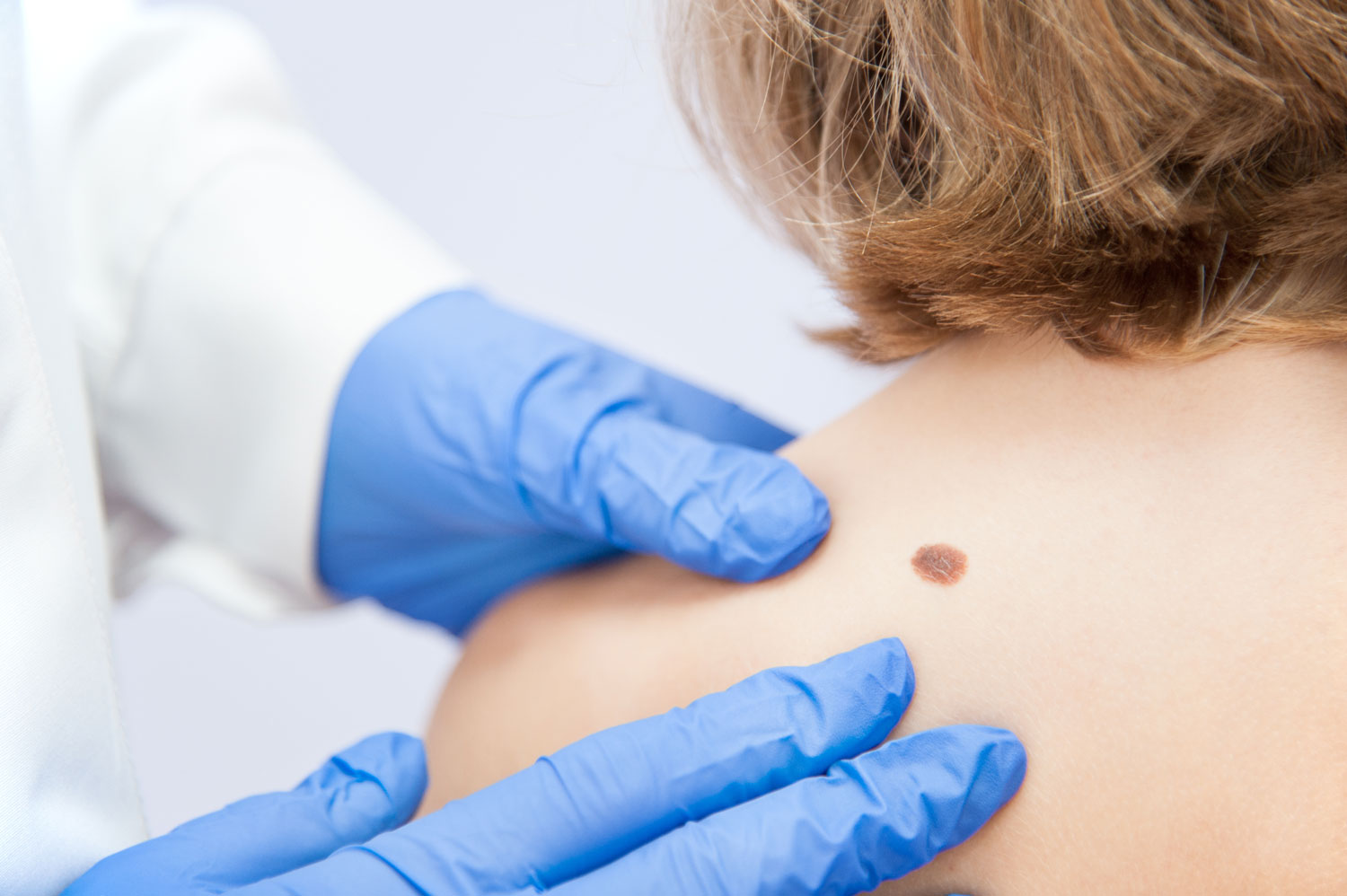
Moles form when skin cells (known as melanocytes) grow together in clusters rather than spreading throughout the skin evenly. While anyone can develop moles, there are a few factors that increase the likelihood of a person having them. These include the following:
- Age
- Genetics
- Hormonal changes associated with pregnancy and other life events
- Frequent sun exposure or sunburns