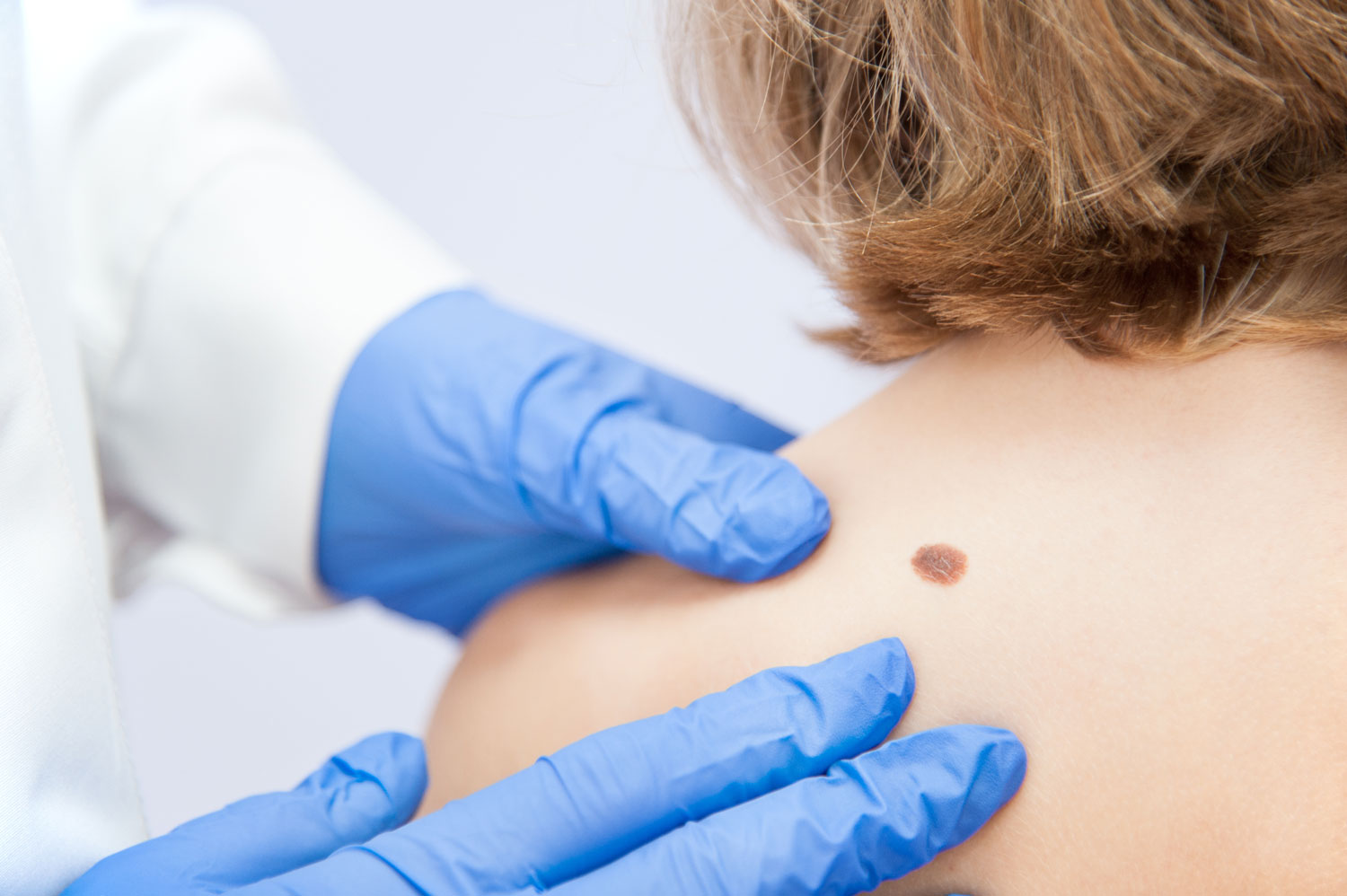
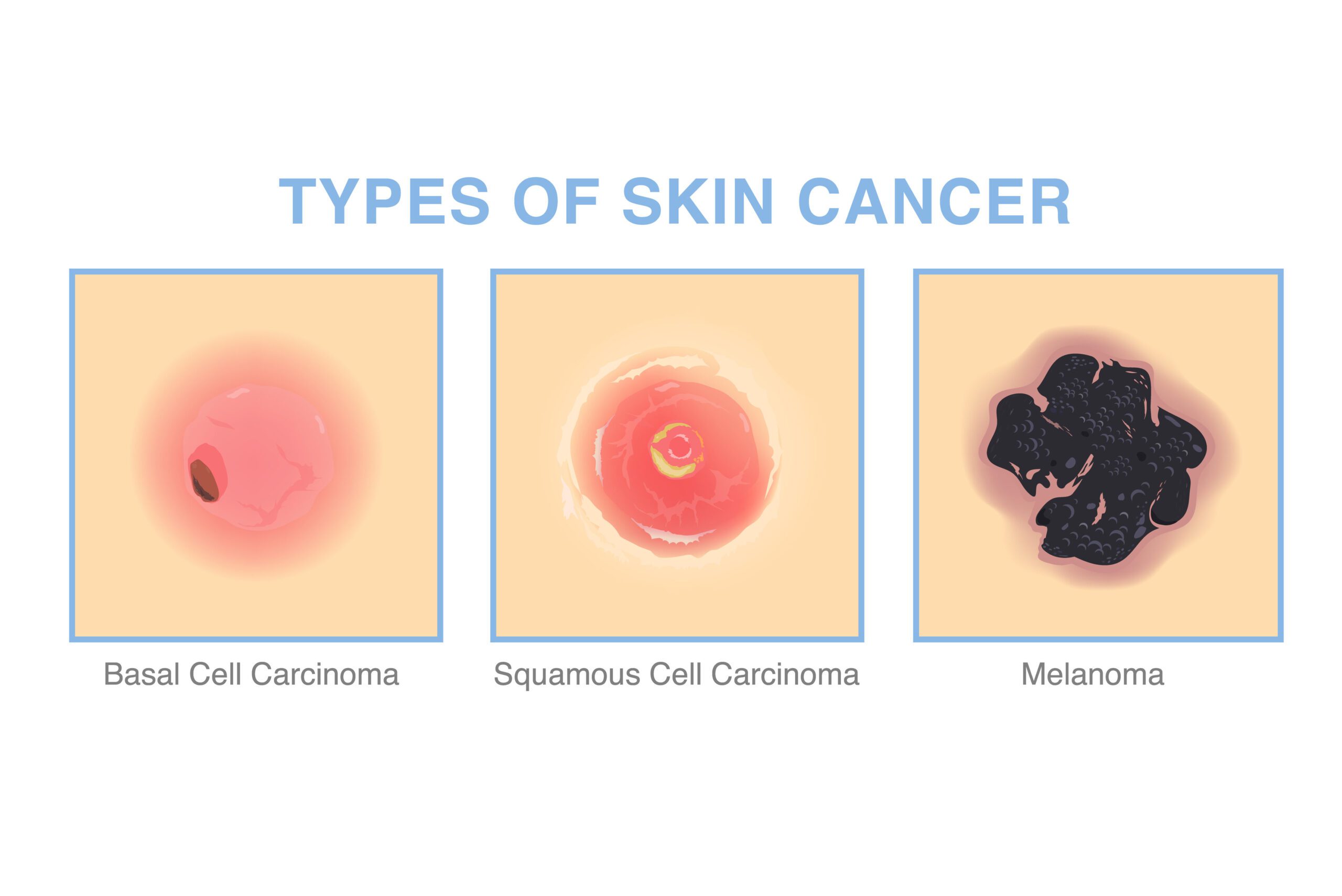
Doctors diagnose more than 9,500 people in the US with skin cancer daily, and two people die of the disease each hour. Today, there are many types of skin cancer, but learning to recognize the signs of each can help ensure early detection, which boosts the 5-year survival rate for some types of melanoma to as high as 99%. This article provides five common skin cancer warning signs and explains how a dermatology team can help you keep your skin healthy.
Skin cancer is a massive concern in the US. An estimated 1 in 5 Americans will develop skin cancer by the age of 70. Fortunately, early detection increases the prognosis for those with a diagnosis – upping the 5-year survival rate for melanoma to 99%, for example.
In this blog, we’ll discuss a few of the most common types of skin cancer and how to detect the early signs of each.
Let’s dive in.
What Causes Skin Cancer?
Skin cancer is a condition classified by the growth of abnormal cells in the epidermis.
While some types of skin cancer have a genetic component, most growths are caused by unrepaired DNA damage caused by the damaging effects of the sun’s UV rays or the use of UV tanning beds.
While there is no way to prevent all instances of skin cancer, avoiding UV tanning beds and taking protective measures, such as wearing sunscreen and UV-blocking clothing when outdoors, can help.
How to Spot Early Signs of Skin Cancer: 5 Things to Look for
The earlier you identify skin cancer, the easier it is to treat. With that in mind, look for these telltale dermatology signs:
1. New moles or blemishes
It could be a sign of skin cancer if you’re older than 21 and you’ve noticed new moles or blemishes popping up on your skin.
Since most people have moles on their bodies, the only reliable way to identify new ones is to conduct regular self-exams.
As such, the Skin Cancer Foundation recommends conducting a head-to-toe self-exam of your skin at least once a month.
This comprehensive exam will serve two purposes: it will familiarize you with the moles you already have on your body and allow you to identify a new one if it pops up.
During this exam, you should inspect all areas of your body, including your face, scalp, hands, arms, torso, upper back, lower back, and legs.
2. Look for spots that change in color, size, shape, or texture
If one of those existing moles begins to change, it could be an early sign of skin cancer.
If melanoma occurs in an existing mole (which happens in an estimated 20-30% of melanoma cases), it may cause said mole to change shape as the cancer grows.
As such, it’s essential to keep the ABCDE rule in mind. Look for spots that are changing in the following ways:
- Asymmetry. The shape of one half of the mole has changed and no longer matches the other side.
- Border. The edges of the mole are becoming ragged, uneven, or blurry.
- Color. The mole has developed new colors. Moles can be a variety of shades of brown, black, and tan. Some also include areas of gray, white, red, or blue.
- Diameter. The diameter of problematic moles tends to be larger than 6 millimeters. In some cases, moles begin small and grow in size.
- Evolving. Any change to a mole is a cause for concern. If a spot or blemish is evolving, visit the dermatologist for a comprehensive exam.
3. Look for spots that are not like the others
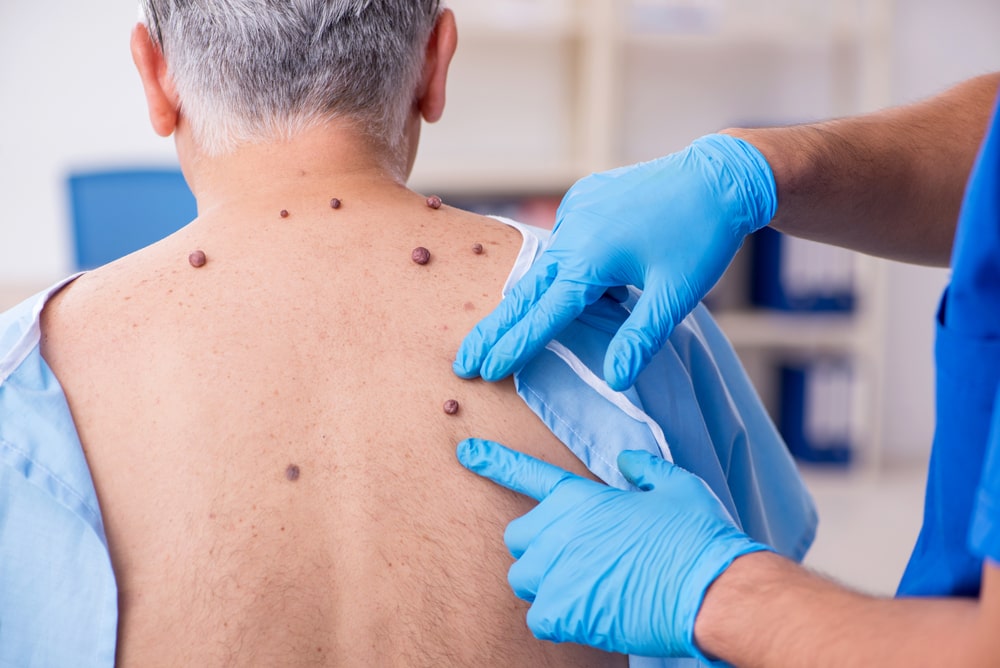
In any area where you have a cluster of moles or spots, look for marks that stand out or look different from the others.
Moles that have an unusual or irregular outline or continuously hurt, itch, crust, or bleed for more than three weeks are a cause for concern.
4. Look for risk areas
Having five or more sunburns in your life doubles your risk for melanoma.
If you’ve spent a lot of time outside or you used to use UV tanning beds, you may have high-risk areas of the body (commonly the forehead, ears, and nose on people who are active outdoors).
You’ll also want to pay special attention to rough skin patches, which could be an early sign of melanoma.
Even if you don’t see any warning signs, it may be wise to visit your dermatologist for a routine check-up anyway.
5. Consider family history
Some skin cancers are hereditary. If you have parents or siblings who have had skin cancer in the past, you may be at increased risk.
Today, experts estimate that about 5-10% of melanoma cases are hereditary.
With that in mind, see your dermatologist more frequently if you know you have a family history of skin cancer. You and your dermatologist can work together to assess your risk and keep an eye on any problem areas.
When it Comes to Skin Cancer, Early Detection Promotes Good Outcomes
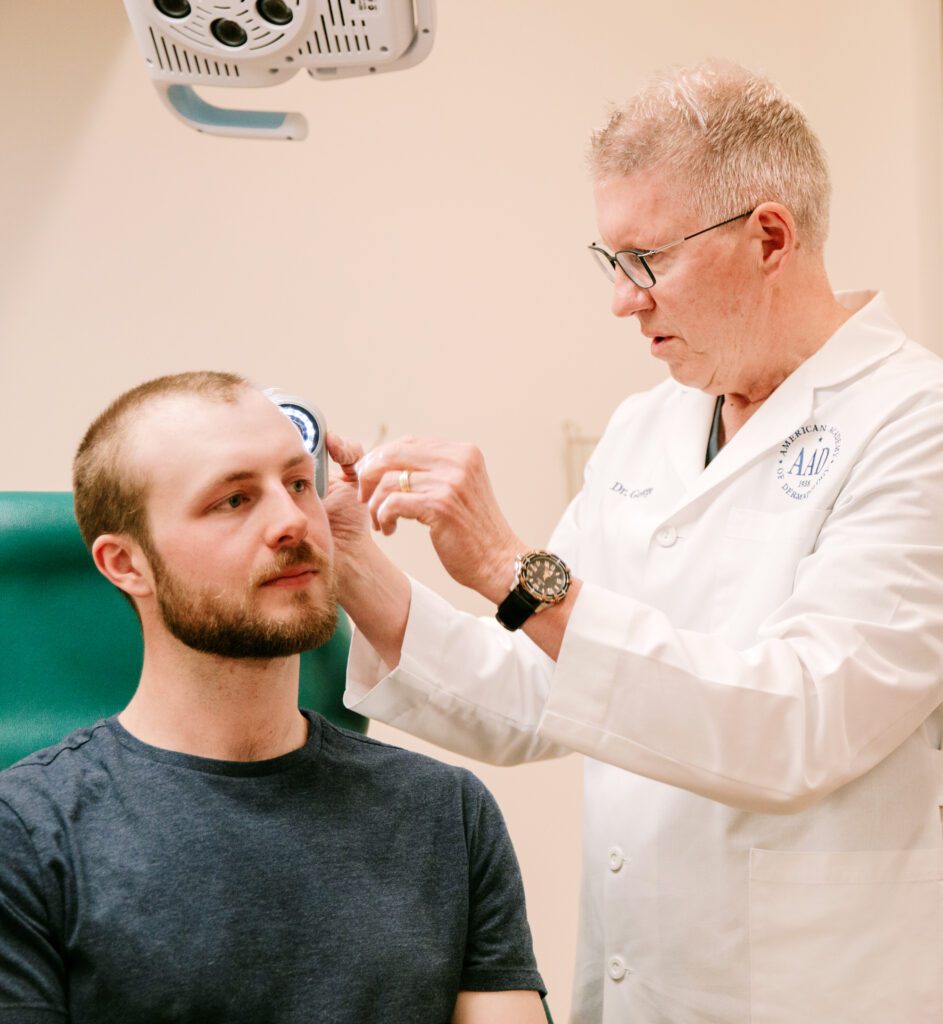
Skin cancer is a frightening disease that can strike even people with no family history of the condition.
Fortunately, it is possible to take a proactive approach. By recognizing common warning signs, like moles that change in size, shape, or color, or moles that don’t blend in with the others on your body, you can keep yourself and your skin safe and healthy for years to come.
Here at Dermatology Associates, our dermatology experts work closely with clients to identify early warning signs of skin cancer through comprehensive skin cancer screenings.
Whether you have an extensive family history of the condition or no known cases in your bloodline, we’ll work with you to spot skin cancer, take preventative steps, and keep your skin healthy for years to come.
Ready to learn more? Contact us today.